Dental implants are modern solutions that replace missing teeth. In this article, we explain the structural elements of an implant and their role in restoring a beautiful smile.
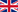
1. Implant body (The screw) The core of the implant is the body (screw), which is placed directly into the jawbone. It acts as an artificial tooth root and provides a stable foundation for the prosthetic crown. This part is usually made of titanium due to its exceptional biocompatibility, which minimizes the risk of allergic reactions or rejection. Titanium is also extremely durable and corrosion-resistant. Placing the screw is the first stage of treatment, followed by osseointegration – the process of the bone fusing with the implant.
2. Abutment (The connector) The abutment is the element that links the implant body with the prosthetic crown. It replaces the natural tooth neck. Its role is to securely hold the crown and transfer chewing forces from the crown to the implant. Abutments can be made of titanium, ceramic, or gold.
3. Prosthetic crown The crown is the visible part that restores the shape, function, and aesthetics of a natural tooth. It is custom-made to match the color and shape of the surrounding teeth. Most crowns are made of porcelain or ceramics, making them indistinguishable from natural teeth.